The Future of Hospitality - The Spectre of the Ghost Kitchen
In the ever-evolving landscape of the hospitality industry, a new player emerged, disrupting traditional restaurant models and offering a glimpse into the future of dining... But was the rapid rise of the ghost kitchen merely a spectral illusion?
"The beauty of ghost kitchens is they can be operated by anyone. (They are) a game-changer in terms of efficiency and flexibility in the culinary world."
Travis Kalanick, Co-founder of CloudKitchens
It is human nature to drive towards efficiency.
In all areas of our existence - from travel, to dining, to household chores - we are always looking for the next "life hack" - a quicker, cheaper, faster way to achieve our end goal.
Of course, this impulse is magnified when it comes to the worlds of industry and commerce, where profit margins, return on investment and bottom lines often seem the only metrics that truly matter.
One such efficiency drive seen in recent years, with a direct bearing on the hospitality industry, was the rise of the 'ghost kitchen'.
Ghost kitchens are commercial facilities built for the preparation of food with the sole purpose of fulfilling delivery orders. Unlike traditional restaurants, they lack dine-in options and storefronts, operating entirely behind the scenes.
Customers place orders through online platforms or apps, and the food is delivered straight to their doorstep. This model eliminates the need for physical restaurants, allowing for a more streamlined, efficient, and cost-effective approach to food service.
The business model behind the ghost kitchen.
A brief history of the ghost kitchen
Intrinsically linked with the food delivery market, we can perhaps trace the origins of the ghost kitchen back to 19th Century Italy where a peckish King Umberto and his queen ordered a pizza delivery to their palace.
Fast-forward around 100 years and the concept of online food ordering started to come to real prominence in the US with the launch of the World Wide Waiter website (now Waiter.com) which offered food delivery to homes and offices from around 60 restaurants in the San Francisco Bay area.
With the rise of mobile technology and app usage in the 21st century, food delivery services such as Just Eat, Deliveroo and Uber Eats grew to contribute to what is now a multi billion-dollar industry.
Of course, the adoption of such services took on even more of a necessity during the Covid pandemic where, set against the backdrop of self-isolation and the need to stay at home, the emergence of ghost kitchens made perfect sense.
For restaurant owners, chefs and delivery services, the ghost kitchen offered a way for businesses to survive through reducing unnecessary overheads, diversifying their offerings and embracing a more streamlined approach to food delivery.
Why go Ghost?
Ghost kitchens offer several advantages for restaurant owners looking to adapt to changing consumer preferences and market dynamics. One of the primary benefits being lower overhead costs.
Without the need for a physical storefront in high-traffic areas, restaurants can save on rent, utilities, and other expenses associated with running a traditional eatery. This cost efficiency allows for higher profit margins, even with lower menu prices.
Of course, markets always follow where consumer demands lead, and several customer trends have contributed to the growth of ghost kitchens.
The rise of digital natives - comfortable with mobile apps and online ordering - has made delivery and takeout a preferred choice for many. At the same time, busy individuals and families appreciate the convenience of having restaurant-quality meals delivered to their doorstep without the time commitment and hassle of cooking or dining out.
Additionally, ghost kitchens provide flexibility and scalability. Restaurateurs can test new concepts and menus without the risk of investing in a brick-and-mortar location.
If a particular concept doesn't resonate with customers, it can be easily replaced or adjusted. This agility allows for quick adaptation to trends and feedback, keeping the business dynamic and responsive.
Moreover, an increasing desire for variety and exotic flavours drives consumers to explore new cuisines through delivery. Ghost kitchens, unconstrained by physical location, can offer a diverse range of options, from gourmet burgers to authentic Thai street food, all within the same delivery radius.

Do ghost kitchens mark the death of the local restaurant?
Rising from the...
The numbers behind the rise of ghost kitchens are staggering. According to a Euromonitor International webinar in 2020, the global online food delivery market was projected to reach $365 billion by 2030, with ghost kitchens playing a significant role in this growth.
Supporting this, a report by Research and Markets estimated that the ghost kitchen market alone was valued at $43.1 billion in 2020 and was expected to reach $115.21 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 11.42% from 2022 to 2030.
As mentioned, the Covid pandemic clearly acted as a catalyst for the rapid expansion of ghost kitchens. With lockdowns and restrictions limiting dine-in options, restaurants had to pivot quickly to meet the rising demand for delivery and takeout.
In fact, according to a report by McKinsey, digital channels for restaurant ordering grew by 30% in 2020, with delivery and takeout accounting for 60-70% of total sales for many restaurants during the period of the pandemic.
Notoriously hard to make good profits from, it is no wonder that more and more dine-in restaurants started to pivot towards the ghost kitchen model and place a much stronger focus on their online delivery business ahead of their physical dining spaces.
Major Players
The rise of ghost kitchens also attracted significant investments from both traditional restaurant chains and leading figures from the tech space.
Companies like Kitchen United, CloudKitchens, and REEF Technology all emerged as major players in the industry, providing infrastructure and support for ghost kitchen operators and developing their own business apps and technology to support their clients' operations.
Kitchen United, for example, operates shared kitchen spaces where multiple restaurants can prepare food for delivery, further reducing overheads and business rate costs.
Tech companies have also made strategic moves into the ghost kitchen space. Uber acquired a majority stake in the ghost kitchen company, CloudKitchens, in 2020, signalling its commitment to expanding its food delivery services, while DoorDash invested in its own ghost kitchen concept, DoorDash Kitchens, allowing restaurants to reach more customers through delivery-only locations.
Traditional restaurants as well as tech companies invested heavily in ghost kitchens.
Spectre at the feast?
While the rise of ghost kitchens clearly enjoyed a pandemic-influenced boom, more recent signs are that initial growth forecasts may have been optimistic.
This is clearly a sector prone to market saturation, with more and more players entering the space over recent years, leading to increased competition and pressure on margins.
Quality is also a concern. Maintaining food standards and consistency across multiple delivery orders and locations is a major challenge, one that operators must address in order to gain customer satisfaction and ensure repeat business.
In the media, the sector has suffered from scrutiny of some dubious investors and questionable business practices. Reports of unhygienic kitchens and faulty tech have inflicted further reputational damage on a market sector that was never imbued with too much industry good will in the first place.
"We have fought and crawled and scraped. We came in there with a dream for our brand, and CloudKitchens tried to destroy it."
Chudi Orubele, Former CloudKitchen operator
Already viewed by many as "the restaurant killer", testimonials such as the above support the (maybe overly romanticised) narrative of the "good guy" local eatery being cannibalised by the "tech bro" and his data-driven delivery model.
Another factor to add to this mix is a strengthening US economy - the market with the largest share of ghost kitchens - which has seen a change in consumer spending habits that indicates a greater willingness to return to traditional restaurant settings, leading to, if not a reduction, then certainly a slow down in the growth of meal delivery service revenues.
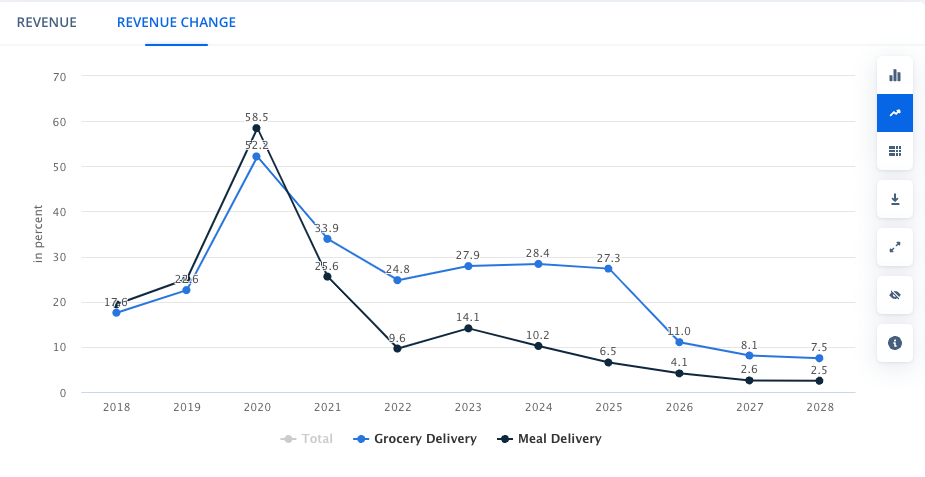
Statista data projecting a reduction in revenue growth for the meal delivery sector over the next four years.
No-one is suggesting that the food delivery market is going anywhere any time soon, but the above data could point to a reversing trend back towards the hybrid model of physical restaurant operators working alongside delivery apps and websites.
While there would still clearly be a space for ghost kitchens in this market, it may not be as big a share of the pie as projections initially forecast.
Not dead yet!
While we may be seeing a rebalancing post-pandemic in the way consumers interact with restaurants and food operators, it is clear that there is still life in the old ghost (kitchen) yet.
As technology continues to advance, with innovations in delivery logistics and order management, ghost kitchens are poised to become even more efficient and responsive to customer demands.
The integration of data analytics and AI-driven insights will also help optimise menu offerings, pricing strategies, and customer engagement, enhancing the overall experience.
It appears the true test of the market space for ghost kitchens will come over the next few years. In a sense, the pandemic years must be viewed an an anomaly - ghost kitchens thrived in a market that was much more dependant on food delivery and where the main competition - physical restaurants - were largely removed from the equation.
Assuming no drastic change in economic or societal factors in up-coming years (a big assumption perhaps) we should see a clearer picture emerge of the size of the ghost kitchen market and how this will exist alongside physical restaurant spaces and other dining providers.
With their focus on delivery and efficiency, virtual establishments are certainly meeting the evolving demands of modern consumers and, as the market continues to grow and evolve, practitioners who offer the most convenience and variety, while remaining uncompromising when it comes to quality, stand the best chance of succeeding.
Whatever the changing face of the dining industry may be, there will always be a space for highly-trained and innovative thinkers to guide its development.
As a hospitality school with a strong, vested interest in the industry's health and prosperity, we will be doing our part to ensure our students are ready for the challenges of tomorrow...
Looking to be a change-maker in the hospitality sector? Contact us below to find out more about our study options...